
CAN Bus – an Introduction
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a revolutionary technology that was developed by Bosch in the 1980s to enable communication between different control units in vehicles without having to rely on a central control unit. The CAN bus quickly spread beyond the automotive industry and is now used in many areas of industrial automation, medical technology and many other applications.
Principles of the CAN Bus
The CAN bus is based on a multi-master principle in which several control devices can send and receive messages, virtually simultaneously via a single communication channel. Messages are prioritized by arbitration on the basis of identifiers, giving priority to messages with lower identifier values.
CAN Bus Technology
The CAN bus is defined by the standards ISO 11898-1 for the data link layer and ISO 11898-2/3 for the physical layer.
Physical Layer
The physical layer of the CAN bus describes the electrical properties and the wiring. Typically, a differential signal is used which offers high immunity to electromagnetic interference.
The data rate of the classic CAN bus can vary depending on the application and network length, allowing speeds of up to 1 Mbit/s. When using CAN FD, data rates of up to 8 MBit/s are possible.
Data Link Layer
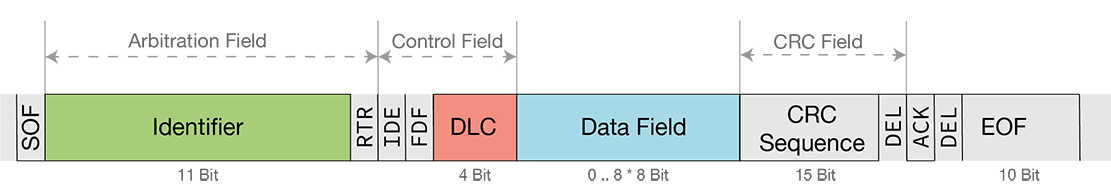
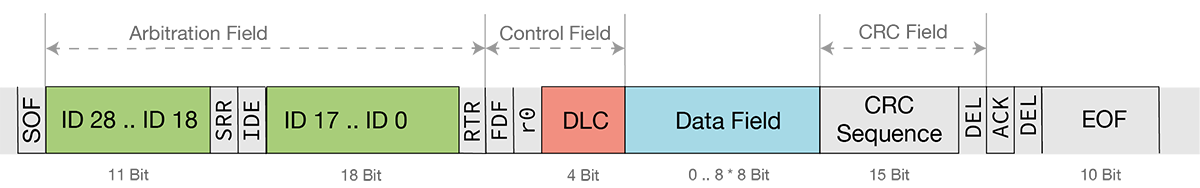
CAN messages consist of an identifier which determines the priority and content of the message, and a data field in which the actual information is transmitted. Either 11 bits (standard frame) or 29 bits (extended frame) are used with the identifier. The data field has a variable length. With CAN Classic, a maximum of 8 bytes can be transmitted.
CAN Bus – Classic Basic Frame Format
CAN Bus – Classic Extended Frame Format
CAN Bus Applications
The CAN bus is widely used in the automotive industry to network components such as engine control units, airbags, ABS and many others. The CAN bus also plays an important role in industrial automation, particularly in controlling and monitoring of machines and production processes. In medical technology, the CAN bus facilitates the networking of medical devices which leads to improved diagnostic options and patient monitoring.
Challenges
Security Concerns
With the increasing networking of systems via the CAN bus, security concerns are also growing. It is crucial to take appropriate measures to protect the systems from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Interoperability
Ensuring interoperability between devices from different manufacturers can be a challenge, especially in heterogeneous networks that support a variety of applications. Interoperability can be ensured by using suitable CAN protocols .
CAN on the internet
For more information on CAN please visit the following websites:
CAN in Automation e.V.
The manufacturer and user organization CAN in Automation offers a wide range of information on CAN. In particular, you will find an overview of higher layer protocols here (e.g. CANopen).
www.can-cia.org
Bosch
The CAN technology was invented by Bosch. If you have any question regarding controllers and licensing, please refer to the website at:
www.bosch-semiconductors.com
You would like to get more information?

+49 2241 - 25 65 9 - 0
Write an email or give us a call.